Long-Term Health Effects of Screen Time on US Children

Increased screen time in US children can lead to several long-term health effects, including eye strain, sleep disturbances, obesity, mental health issues like anxiety and depression, and potential cognitive and developmental delays, making it crucial to monitor and balance screen usage with other healthy activities.
Are you concerned about the potential long-term health effects of increased screen time on your children? With the proliferation of smartphones, tablets, and computers, children in the US are spending more time than ever in front of screens. Let’s explore the potential risks and what you can do to mitigate them.
Understanding the Rise of Screen Time Among US Children
In today’s digital age, screens are ubiquitous. From smartphones and tablets to televisions and computers, children in the United States are surrounded by digital devices. This increase in screen time has led to concerns about its potential long-term health effects, making it important to understand the extent of this phenomenon.
The amount of time children spend on screens has risen dramatically over the past few decades, reshaping their daily routines and activities. Understanding this increase is the first step in addressing its potential impact on their well-being.
Factors Contributing to Increased Screen Time
Several factors contribute to the increased screen time among US children. Access to devices, availability of engaging content, and changes in lifestyle all play a role.
- Device Availability: The widespread availability of smartphones and tablets has made it easier for children to access screens at any time.
- Engaging Content: Streaming services, social media, and video games offer endless entertainment, capturing children’s attention for extended periods.
- Lifestyle Changes: As traditional outdoor activities decline, screen-based entertainment often fills the void, especially during leisure time.

Data on Screen Time Usage
Research indicates that children in the US spend a significant portion of their day using screens. The numbers are particularly concerning as children are spending less time on physical activity.
Studies have shown that, on average, children aged 8-12 spend 4-6 hours daily watching or using screens. Teenagers can spend up to 9 hours per day engaging with digital media. These statistics highlight the scale of screen time in children’s lives.
In conclusion, the rise of screen time among US children is a multifaceted issue driven by device availability, engaging content, and lifestyle changes. Understanding the factors and data surrounding this trend is vital for addressing its long-term health effects.
Potential Eye Health Issues
One of the most immediate and tangible concerns associated with increased screen time is its impact on eye health. Prolonged screen use can lead to several eye-related issues, affecting children’s comfort and vision.
While these issues are often temporary, chronic or excessive screen time can potentially contribute to more serious long-term problems. Let’s explore the potential eye health issues to raise awareness.
Digital Eye Strain
Digital eye strain, also known as computer vision syndrome, is a common condition resulting from prolonged use of digital devices. It can impact children’s learning and cognitive abilities.
Symptoms of digital eye strain include eye fatigue, blurred vision, headaches, and dry eyes. These symptoms can disrupt daily activities and academic performance.
Myopia (Nearsightedness)
Studies suggest a potential link between increased screen time and the development of myopia, or nearsightedness, in children. Excessive near work, such as focusing on screens, can strain the eyes and contribute to vision changes.
Research indicates that children who spend more time outdoors and less time engaging in prolonged near work have a lower risk of developing myopia. This implies that physical activity and outdoor exposure do contribute to healthier vision.
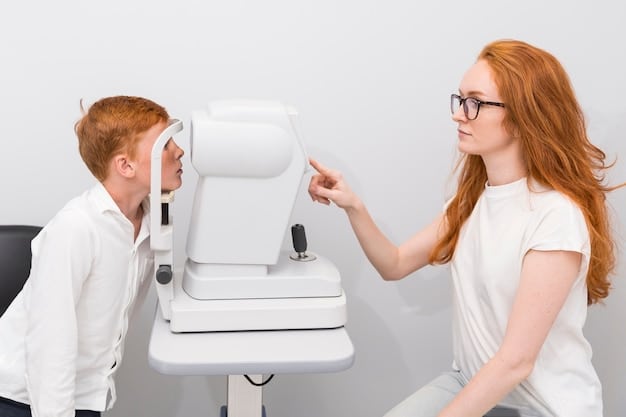
To mitigate potential eye health issues, it is crucial to implement strategies such as the 20-20-20 rule (taking a 20-second break every 20 minutes to look at something 20 feet away), encouraging outdoor activities, and scheduling periodic eye exams. These measures can help protect children’s vision and promote overall eye health.
In summary, the potential eye health issues associated with increased screen time are significant and warrant attention. Digital eye strain and the development of myopia are primary concerns that can be addressed through preventive measures and proactive eye care.
Sleep Disturbances and Screen Time
The relationship between screen time and sleep patterns is a critical area of concern, as adequate sleep is essential for children’s physical and cognitive development. Increased screen time, particularly before bed, can disrupt sleep patterns and lead to numerous health issues.
The consequences of sleep disturbances extend beyond mere tiredness, affecting various aspects of children’s well-being. Let’s explore the various disruptions to address ways to combat this.
Impact on Sleep Quality
The blue light emitted by screens can interfere with the production of melatonin, a hormone that regulates sleep. This can make it harder for children to fall asleep and reduce the overall quality of their sleep.
Studies have shown that exposure to blue light suppresses melatonin secretion, leading to increased alertness and delayed sleep onset. These findings highlight the importance of minimizing screen exposure before bedtime.
Consequences of Sleep Deprivation
Chronic sleep deprivation can have significant consequences for children, affecting their cognitive function, mood, and physical health. This could alter their learning and general health.
- Cognitive Impairment: Lack of sleep can impair attention, memory, and problem-solving skills, affecting academic performance.
- Mood Disorders: Sleep deprivation is linked to increased irritability, anxiety, and depression in children.
- Physical Health: Insufficient sleep can weaken the immune system, increase the risk of obesity, and disrupt metabolic processes.
To promote healthy sleep habits, it is recommended to establish a consistent bedtime routine, avoid screen exposure at least one hour before bed, and create a sleep-friendly environment. These strategies can help children get the restful sleep they need to thrive.
In conclusion, sleep disturbances resulting from increased screen time pose a serious threat to children’s health and well-being. Understanding the impact on sleep quality and the consequences of sleep deprivation is essential for promoting healthy sleep habits and supporting optimal development.
Obesity and Sedentary Behavior
Increased screen time is often associated with sedentary behavior, which contributes to the rising rates of childhood obesity in the US. Spending excessive time in front of screens reduces physical activity and can lead to poor dietary habits, both of which are significant risk factors for obesity.
The implications of childhood obesity are far-reaching, affecting both short-term and long-term health outcomes. Let’s explore the causes and the implications, so that we can understand how to avoid it.
Link Between Screen Time and Physical Activity
Children who spend more time watching screens are less likely to engage in physical activities. This decrease in physical activity contributes to weight gain and overall poor health.
Studies have shown that each additional hour of screen time per day is associated with a higher risk of obesity. This highlights the importance of balancing screen time with physical activities to maintain a healthy weight.
Impact on Dietary Habits
Screen time can also influence dietary habits. Children often consume unhealthy snacks and sugary drinks while watching screens, which can lead to weight gain and poor nutrition. It’s easy to overeat without paying attention.
- Snack Consumption: Children are more likely to snack on high-calorie foods while watching screens.
- Marketing Influence: Advertisements for unhealthy foods often target children during screen time, influencing their food choices.
- Reduced Mealtime Focus: Eating in front of screens can lead to mindless eating and overconsumption.
To combat obesity, it is essential to limit screen time, encourage regular physical activity, and promote healthy eating habits. Setting boundaries around screen use and promoting active play can help children maintain a healthy weight and reduce the risk of obesity-related health problems.
In summary, the link between obesity and sedentary behavior resulting from increased screen time is a significant public health concern. Addressing this issue requires a multifaceted approach that includes limiting screen time, promoting physical activity, and fostering healthy dietary habits.
Mental Health Issues and Emotional Well-being
The impact of increased screen time extends beyond physical health, significantly affecting children’s mental health and emotional well-being. Excessive screen use has been linked to various mental health issues, including anxiety, depression, and social isolation.
The digital world, while offering numerous benefits, can also pose challenges to children’s emotional and psychological development. Let’s explore how to ensure these mental issues can be handled.
Association with Anxiety and Depression
Studies have found a correlation between increased screen time and higher rates of anxiety and depression in children. The constant exposure to social media and online content can trigger feelings of inadequacy, social comparison, and low self-esteem.
Research indicates that children who spend excessive time on social media are more likely to report symptoms of depression and anxiety. This highlights the importance of monitoring children’s online activities and providing support for their emotional well-being.
Social Isolation and Loneliness
While screens can facilitate social interaction, excessive screen time can also lead to social isolation and loneliness. Spending too much time online can reduce face-to-face interactions, affecting children’s ability to develop social skills and form meaningful relationships.
Children who primarily interact with others online may struggle with real-world social situations, leading to feelings of isolation and loneliness. Encouraging offline social activities and promoting positive social interactions can help mitigate these risks.
To support children’s mental health, it is essential to promote healthy screen habits, encourage open communication about online experiences, and provide access to mental health resources when needed. These strategies can help children navigate the digital world while protecting their emotional well-being.
In conclusion, the mental health issues and emotional well-being of children are significantly impacted by increased screen time. Addressing this issue requires a comprehensive approach that includes promoting healthy screen habits, fostering open communication, and providing access to mental health support.
Cognitive and Developmental Effects
The long-term cognitive and developmental effects of increased **screen time** on children are a growing area of concern for researchers and educators. Excessive screen use can impact attention spans, learning abilities, and overall cognitive development.
Understanding these potential effects is crucial for promoting healthy cognitive growth in children. Let’s explore the different areas it could impact and address ways to help combat it.
Impact on Attention Spans
Studies suggest that increased screen time, especially exposure to fast-paced content, can shorten attention spans and impair children’s concentration skills. The constant stimulation from screens can make it difficult for children to focus on tasks that require sustained attention.
- Attention Deficit: Excessive screen time is associated with an increased risk of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms in children.
- Cognitive Distraction: Frequent interruptions from notifications and online content can disrupt cognitive processes and reduce learning efficiency.
- Impaired Focus: Children who spend more time on screens may struggle to focus on academic tasks and other activities that require attention.
Effects on Learning and Academic Performance
Excessive screen time can negatively impact learning and academic performance. Engaging in screen-based activities for prolonged periods can reduce the time available for reading, studying, and other educational pursuits.
Research indicates that children who spend more time watching screens tend to have lower academic achievement. This highlights the importance of balancing screen time with educational activities to support cognitive development.
To promote healthy cognitive development, it is recommended to limit screen time, encourage reading and other educational activities, and provide opportunities for creative play and exploration. These strategies can help children develop strong cognitive skills and achieve academic success.
In summary, the cognitive and developmental effects of increased screen time on children are significant and warrant attention. Addressing this issue requires a comprehensive approach that includes limiting screen time, promoting educational activities, and fostering creative play.
| Key Area | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| 👀 Eye Health | Prolonged use can cause eye strain and potentially myopia. |
| 😴 Sleep Patterns | Blue light disrupts melatonin, affecting sleep quality. |
| 🏋️ Obesity | Reduces physical activity, impacting dietary habits. |
| 🧠 Cognitive Skills | May impact attention spans and learning abilities. |
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
▼
The major concerns include eye strain, sleep disturbances, obesity, mental health issues such as anxiety and depression, and negative impacts on cognitive and social development.
▼
Encourage the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds. Ensure proper lighting and regular eye exams.
▼
Establish a consistent bedtime routine, avoid screen use at least one hour before bed, and create a dark, quiet, and cool sleep environment.
▼
Limit screen time, promote outdoor activities, encourage healthy snacking, and ensure balanced meals with plenty of fruits and vegetables.
▼
Encourage open communication, monitor online activities, teach healthy social media habits, and seek professional help if the child shows signs of depression or anxiety.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the increased screen time among US children presents a complex challenge with far-reaching health implications. Addressing this issue requires a coordinated effort involving parents, educators, and healthcare professionals to promote healthy screen habits and support the overall well-being of children in the digital age.